ERP and Quality
Software & Analysis
In automotive plastics manufacturing. By Louis Columbus
By most accounts, this year will be better for the automotive sector than 2021 when the industry lost about $210 billion in revenue, according to consulting firm AlixPartners. However, improvements may only be marginal as automakers and their suppliers continue to face product shortages.
One of the segments likely to face the greatest challenges in 2022 are automotive plastics manufacturers who will continue to face shortages of the raw materials, composites and resins required for both interior and exterior vehicle parts. To offset shortages and supply chain unpredictability, these manufacturers will need to increase productivity and agility, keep costs in check, and potentially identify and design around alternative plastics materials—even as they ensure compliance with government and industry standards for quality and safety.
The pace of change in today’s volatile global market means that it is nearly impossible to rely on manual systems for decision-making, workflow management, and reporting. Instead, plastics automotive manufacturers need to leverage a combination of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and quality management systems supported by a common set of real-time production and process reporting data.
Automation via ERP and Quality Management is Key to Continuity
Increasingly, automotive plastics manufacturers are investing in ERP and quality management software to understand how tradeoffs between maintaining quality and increasing production speed, as well as the impact on costs. Notably, the cost of quality (CoQ) can account for 15% to 20% of sales and between three to five times the size of net profits in a given year, according to the American Society for Quality (ASQ). Through the combination of ERP and quality management, it is possible to gain a 360-degree view of the shop floor, see how machine yield rates help keep standard cost variances in check, and measure if and by how much quality improves production efficiency.
The need for real-time production and process reporting data shared across ERP and Quality Management systems is essential for automating automotive plastics manufacturing workflows. Consider how the type of resins used can affect the variation in machine yields, work instructions, ancillary tools, and training of operations. Real-time production and process monitoring data serve multiple purposes in identifying how, why, and how much product quality varies over time.
“We added real-time production monitoring, so we could see what was happening on the shop floor without having to walk around,” said a production material control manager at an automotive plastics company. “This allows us to step up our processes where we might be having a problem, and when used with shop data, it lets our operators can see what a machine is doing and be proactive in catching issues before they get out of hand.”
Real-time production and process data can also be applied to statistical process control (SPC) analysis, one of the truest measures of quality for the plastics industry. For example, SPC techniques can be used to identify incomplete mold fills and corresponding excessive barrel temperature spikes to improve root cause analysis. Likewise, combining SPC data with ERP and quality management software can help to understand why a given mold isn't filling with material and its potential for overheating; more broadly, this combination serves as a valuable resource for supporting audits.
“We wanted an integrated ERP and quality management system that understood our particular business, including family molds and multiple cavitations running at the same time,” the production material control manager noted. “Not only was this important in terms of efficiency and maintenance; as a supplier to major automakers, we also had to comply with our automotive customers’ quality standards and business transaction requirements.”
AdCreative Missing.
(double-click to add)
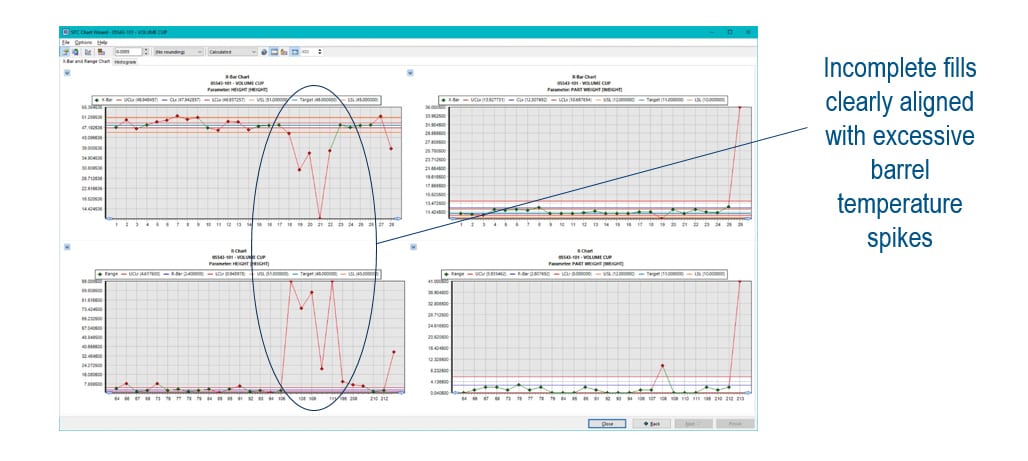
Figure 1. How Automotive Plastics Manufacturers Use SPC and Root Cause Analysis. Source: DELMIAWorks
Key ERP and Quality Management Features to Consider
Whether seeking to optimize existing systems or add new capabilities, the goals in evaluating any ERP and quality management software are gaining the needed visibility and control over how every aspect of production impacts product quality and costs—as well as achieving the manufacturer’s quality, financial and customer-driven goals. With those goals in mind, following are eight key questions to ask.
Can the ERP and quality management access real-time production and process monitoring data? Real-time production and process monitoring data enables automotive plastics manufacturers to set performance baselines and track cost variances, keeping production schedules on track. Moreover, it is essential for gaining a 360-degree view of the shop floor, staying in compliance with regulatory requirements, and strengthening their financial control by improving shop floor visibility to the order level.
"We consider ourselves data-driven now,” said the CFO of a leading automotive plastics manufacturer. “The system has allowed us to come in alongside our employees and show them that the information can support them and make them better molders."
Is EDI expertise supported? EDI is a core requirement of doing business in the automotive industry and can potentially save thousands of hours and dollars a year. Look for ERP and quality management solutions capable of automatically translating incoming EDI files and updating all related records. The same holds true for outgoing files that need to be automatically transferred back to customers and suppliers. Having EDI functionality capable of this workflow reduces the time and errors related to manual data entry.
“Our customers want quality parts, in the correct quantity, on time, and at a competitive price,” explained the plastics production manager at a midwestern automotive manufacturing firm. “In the automotive industry, EDI is a major component in a supplier’s ability to deliver what automakers want.”
What support exists for core production and quality management foundational metrics? Automotive plastics manufacturers need to have ERP and quality management functionality in place that helps explain why there are variations in production run rates and yield rates by machines, as well as see how yield variations and wide swings in SPC charts impact the financials.
Understanding cost, price, and production variances is another benchmark to consider. The software should support engineering change order (ECO) tracking and audits, including the ability to tie them back to specific raw material lots and production runs. The same holds for return material authorization (RMA) analysis.
What capabilities are available to support traceability and audits? For example, the ability to:
- Track and report variability reduction, cycle time reduction, and risk mitigation across every shop floor and then aggregate the data together to quantify risk financially.
- Produce supplier audits, and publish the data on a secured corporate Intranet site, with a series of analytics and metrics included to track trends in their performance over time.
- Manage suppliers to consistent, high-quality standards on a global basis and audit their inbound deliveries, posting and sharing their quality results individually and company-wide.
- Use product quality metrics with suppliers to gain access to more materials. As suppliers are constrained for materials, define shared quality goals that, when met, lead to more purchases.
- Support creating and fine-tuning non-compliance/corrective action (NC/CA) programs to evaluate a supplier's inbound orders and find new ways of reducing defective raw materials shipments, avoiding wrong orders, and minimizing late deliveries.
- Customize corrective action/preventative action (CAPA) to an automotive plastics manufacturer's workflows—a must-have for continually improving compliance and quality management.
- Support tooling audit and compliance to the mold level. Knowing which tools and molds have been the most and least problematic and what's being done to keep them working correctly is essential.
Is integrated financial reporting included? Activity on the production floor needs to be translated into financial results, making integrated financial reporting one of the most important features in an automotive plastics manufacturing ERP system. Tracking how changes in production planning, scheduling, and continual improvements in workflows translate into costs savings and additional revenue are a must-have.
How broad is the manufacturing resource planning support? Minimally, automotive plastics manufacturers need support for requirements planning, master production schedule (MPS), capacity planning, bill of materials (BOM), shop floor control, and project management. These functional areas make it possible to operate a production center efficiently, tracking performance back to financial reporting. Ideally, these modules are integrated into a common database or system of record.
What manufacturing Execution System (MES) functionality is included? MES manages daily scheduling on the production floor, taking into account MPS workflows and BOM requirements, factoring in the skill sets of machine operators. Whether separate software or integrated into the ERP system, best-in-class MES can take all these factors into account and drastically reduce the time to produce a product.
How much can supply chain management (SCM) flex in response to production needs? Suppliers and the supply chains they comprise are the most important relationships to any automotive plastics manufacturer. In evaluating systems, be sure to look for SCM functionality that supports demand planning, logistics and transportation management, procurement and sourcing, quality management, supply chain planning, and execution of drop shipments.
Conclusion
Maintaining business continuity means finding effect strategies for managing shortages and supply chain unpredictability. These may include increasing productivity and agility, keeping costs and revenues in check, and turning to alternative plastics materials and suppliers. The combined capabilities of ERP and quality management software—fueled by real-time production and process data—empower automotive plastics manufacturers to adopt these strategies while maintaining compliance with government and industry standards for quality and safety. In turn, by bringing business continuity, predictability and quality to their operations, these manufacturers are well-positioned to grow both their customers and profits.
Evaluation Framework for ERP and Quality Management Systems
Maintaining business continuity means finding effect strategies for managing shortages and supply chain unpredictability. These may include increasing productivity and agility, keeping costs and revenues in check, and turning to alternative plastics materials and suppliers. The combined capabilities of ERP and quality management software—fueled by real-time production and process data—empower automotive plastics manufacturers to adopt these strategies while maintaining compliance with government and industry standards for quality and safety. In turn, by bringing business continuity, predictability and quality to their operations, these manufacturers are well-positioned to grow both their customers and profits.
